Beyond Fossil Fuels: The Path Towards Zero Carbon and Sustainable Agriculture
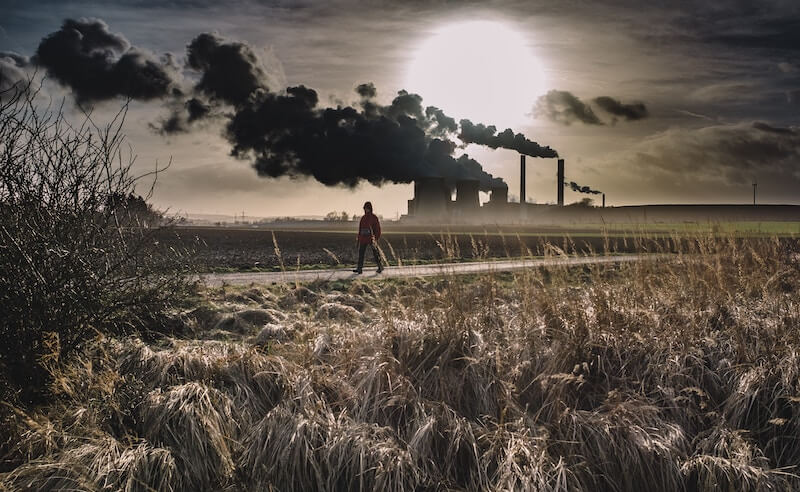
Ever since the industrial revolution, the inclusion of fossil fuels in agriculture has been instrumental in updating farming practices. These energy sources: coal, oil, and natural gas, are used to power farm equipment and produce chemicals needed for synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. However, despite their significance, the adverse environmental repercussions of their use are progressively more noticeable. Consequently, there is a growing demand for the transition from fossil fuel-dependent practices to more comprehensive and environmentally sustainable agricultural methods.
The use of Fossil Fuels in Agriculture
The types of fossil fuels used in agriculture are varied. Diesel fuel is commonly used to operate machinery such as tractors, combines, and irrigation systems. Natural gas and propane are also used in some agricultural machinery and as a source of heat for drying crops. In certain regions globally, coal serves as a primary energy source for generating electricity, which in turn powers various agricultural operations like irrigation pumps and processing facilities.
Synthetic Chemicals made from Fossil Fuels Contaminate Soil and Water
The integration of fossil fuels into agricultural practices poses several significant environmental challenges. The burning of these fuels release carbon dioxide and various other greenhouse gases, thereby intensifying the global climate change dilemma. Moreover, the creation of synthetic chemicals derived from fossil fuels risks soil and water contamination, negatively affecting both human health and the broader environment.
The procedures involved in the extraction, transportation, and utilization of fossil fuels can further disrupt ecosystems, leading to environmental concerns such as air and water pollution, devastation of wildlife habitats, and a decrease in biodiversity. Synthetic substances, including fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides commonly produced from fossil fuels, are prevalent in contemporary farming practices. These materials can jeopardize both soil health and water quality, while also posing dangers to human health. Studies in environmental science have indicated that the persistent use of these chemicals leads to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, constituting a threat to human health.
Fossil fuels are also used to operate processing plants that turn raw agricultural products into finished goods. Processing and packaging facilities in the agricultural sector require substantial energy, which leads to further greenhouse gas emissions and subsequent environmental consequences. Furthermore, the global transportation of agricultural commodities is heavily dependent on fossil fuels. Vehicles like trucks, trains, and ships consume enormous quantities of diesel fuel to distribute food products worldwide, thereby increasing the overall environmental footprint.
Transitioning from Fossil Fuels: The Future of Agriculture
The urgency to transition away from the usage of fossil fuels in agriculture is escalating. By implementing sustainable agricultural methods like organic farming, agroforestry, geothermal greenhouses, and permaculture, we can diminish our dependency on these fuels. Embracing sustainable agricultural practices will enhance the health of the soil, the quality of water, and the richness of biodiversity. These practices can also help sequester carbon in the soil, mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Besides adopting sustainable agricultural methods, integrating renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal power into farming operations can be instrumental. These alternative energy sources are not just more eco-friendly, but also come with the additional advantage of reducing the climate change impacts associated with the combustion of fossil fuels. Their adoption can play a pivotal role in minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and other adverse environmental effects.
Growing To Give’s Sustainable Agriculture Initiatives
Agriculture's dependence on fossil fuels has substantially impacted our environment negatively. Therefore, there's an urgent requirement to shift from this reliance on fossil fuels. Environmentally friendly farming methods, such as those implemented in the Growing To Give agricultural initiatives, can mitigate agriculture's ecological footprint and foster a more comprehensive and sustainable strategy for food production.


.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)