The Role Rewilding Plays in Shaping the Future of Our Environment
Rewilding is a progressive approach to conservation. It's about letting nature take care of itself, enabling natural processes to shape land and water, repair damaged ecosystems and restore degraded landscapes. Through rewilding, wildlife's natural rhythms create wilder, more biodiverse habitats.
This concept is not only about returning areas of land to a state of wilderness but also about allowing nature to find its own way. It involves minimal human intervention and the reduction or removal of management practices such as animal grazing. The idea is to allow ecosystems to evolve naturally, fostering resilience through diversity.
The concept of rewilding has its roots in the recognition that natural processes, such as predation and natural disturbances like fire, are crucial for maintaining biodiversity. It's about reintroducing these processes, or allowing them to resume where they have been suppressed, and then stepping back.
The Importance of Rewilding in Ecosystem Restoration
By allowing nature to take its course, rewilding can help reverse the negative impacts of human activities, such as deforestation, overgrazing, and pollution. Ecosystem restoration through rewilding involves the reintroduction of keystone species that play a critical role in maintaining the structure of a native ecological community.
Ecosystem restoration is critical for the survival of many species. By creating more diverse habitats, rewilding a degraded environment can provide homes for a wide range of animals and plants, many of which are currently under threat. The process also helps to restore natural processes like nutrient cycling and natural burn cycles, which are essential for the health of a natural ecosystem.
The benefits of ecosystem restoration through rewilding go beyond biodiversity. Restored ecosystems can store and sequester carbon, helping to mitigate climate change. They can also help to regulate water flow, reducing the risk of floods and droughts.
How Rewilding Contributes to Environmental Rehabilitation
Environmental rehabilitation is another crucial aspect of rewilding. This process involves restoring damaged ecosystems so that they can support life again. It's about giving nature a helping hand to recover from the environmental degradation caused by activities such as mining, deforestation, and pollution. Rewilding plays a critical role in land reclamation.
Rewilding contributes to environmental rehabilitation by allowing natural processes to take over. For example, in areas affected by deforestation, rewilding can lead to the natural regeneration of forests. In places impacted by pollution, the process can result in the restoration of clean water and healthy soil.
Moreover, rewilding can also contribute to environmental rehabilitation in urban areas. By creating green spaces and corridors, rewilding can provide habitats for wildlife and improve the quality of life for city dwellers. Urban rewilding projects can also help to mitigate the effects of climate change by reducing urban heat islands and improving air quality.
The Role of Rewilding in Biodiversity Recovery
Rewilding plays a vital role in biodiversity recovery. By allowing nature to take its course, we can create more diverse habitats where a wide range of species can thrive. This process involves the reintroduction of native species, the restoration of natural processes, and the creation of larger, more connected areas of wilderness.
Biodiversity recovery is essential for the health of our planet. It helps to ensure the resilience of ecosystems in the face of change, allowing them to recover more quickly from disturbances. A higher level of biodiversity also means that ecosystems can provide a wider range of ecosystem services including pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration.
Biodiversity recovery is essential for the health of our planet the health of our planet. It helps to ensure the resilience of ecosystems in the face of change, allowing them to recover more quickly from disturbances. A higher level of biodiversity also means that ecosystems can provide a wider range of ecosystem services including pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration.
Habitat Regeneration Through Rewilding
Habitat regeneration is a key aspect of rewilding. This process involves restoring degraded habitats so that they can support life again. It's about recreating the conditions that these habitats need to thrive, whether it's a wetland, a forest, or a grassland.
Rewilding achieves habitat regeneration by allowing natural processes to take over. For example, in a degraded forest, this might involve allowing the trees to grow back naturally, without human intervention. In a drained wetland, it might mean reintroducing water and allowing the ecosystem to adjust, adapt and regenerate
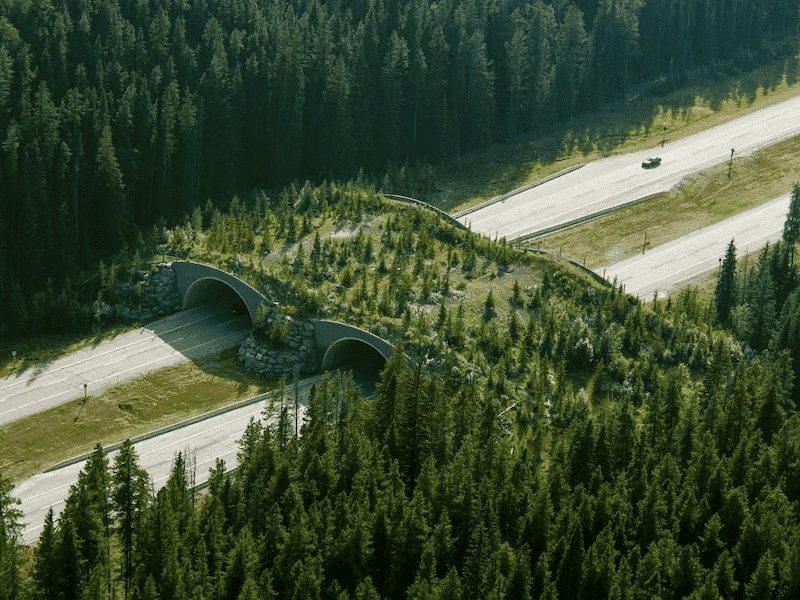
Habitat regeneration through rewilding also involves creating connections between habitats. By creating corridors of wilderness, we can allow wildlife to move freely between different areas, increasing their chances of survival like the wild way bridges we see that cross out highways.
Rewilding as a Conservation Effort
Rewilding is a powerful tool in the field of conservation. Traditional conservation efforts often focus on protecting individual species or maintaining habitats in a certain state. Rewilding, on the other hand, is about allowing nature to find its own way, creating wilder, more biodiverse habitats.
Rewilding as a conservation effort is about creating self-sustaining ecosystems that are resilient to change. It's about reintroducing natural processes and stepping back, allowing nature run its course. This approach can be more effective and sustainable in the long term than traditional conservation efforts.
Moreover, rewilding can also help to raise awareness about the importance of conservation. By creating wilder, more biodiverse spaces, we can inspire people to value and protect nature.
The Impact of Rewilding on Natural Resource Management
Rewilding has significant implications for natural resource management. By allowing ecosystems to recover and become more resilient, we can ensure the sustainable use of natural resources. For example, healthy forests can provide a sustainable supply of timber, while restored wetlands can purify water. Natural resource management is not just about the sustainable use of resources, but also about their equitable distribution. Rewilding can contribute to this by helping to regulate ecosystem services. By restoring forests, we can help to regulate water flow and reduce the risk of floods and droughts.
Rewilding can also help to mitigate the impacts of climate change on natural resource management. By restoring ecosystems and allowing them to sequester carbon, we can help to reduce the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere, mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Rewilding as a Conservation Effort
Rewilding is key to maintaining ecological balance. By restoring natural processes and reintroducing keystone species, we can ensure the intended functioning of ecosystems. For example, predators can control the population of herbivores, preventing overgrazing and promoting the growth of vegetation.
Ecological balance is crucial for the health of our planet. It ensures the resilience of ecosystems, allowing them to recover from disturbances and adapt to change. By maintaining ecological balance, we can ensure the provision of ecosystem services, from pollination to water purification.
Rewilding can help to restore ecological balance in degraded ecosystems. By reintroducing natural processes and allowing nature to take over, we can recreate the conditions that these ecosystems need to thrive.
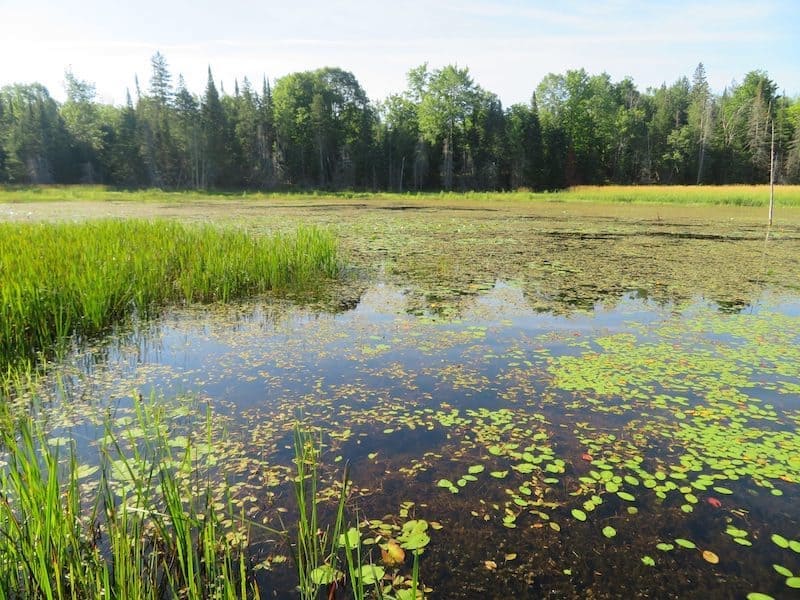
The Role of Rewilding in Wetland Restoration
Rewilding plays a crucial role in wetland restoration. By reintroducing water and allowing nature to take its course, we can restore degraded wetlands and create more diverse, resilient ecosystems. This process involves the reduction or removal of human constructed drainage systems and agriculture, and replacing them with natural processes like nutrient cycling. Wetland restoration is crucial for the health of our planet. Wetlands provide a wide range of ecosystem services, from water purification to flood protection. They also provide homes for a wide range of species, many of which are currently endangered or under threat.
Wetland restoration through rewilding can also contribute to the fight against climate change. Wetlands are among the most carbon-rich ecosystems on the planet, and their restoration can help to sequester carbon and reduce the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Rewilding for Climate Resilience
Rewilding can contribute significantly to climate resilience. By restoring ecosystems and allowing them to sequester carbon, we can help to mitigate the impacts of climate change. Climate resilience is crucial in the face of the ongoing climate crisis. It's about being able to withstand the impacts of climate change, from rising temperatures to more frequent and intense storms. By creating more resilient ecosystems through rewilding, we can help to buffer these impacts and ensure the survival of a wide range of species.
Rewilding can also contribute to climate resilience by helping to regulate climate at the local and regional level. For example, forests can help to regulate temperature and rainfall patterns, while wetlands can help to buffer against sea-level rise and storm surges.
The Reintroduction of Native Plant and Animal Species Through Rewilding
Rewilding involves the reintroduction of native plant and animal species. By bringing back these species, we can restore natural processes and create more diverse, resilient ecosystems. This process involves careful planning and monitoring to ensure the survival of the reintroduced species and the health of the ecosystem.
The reintroduction of native species is crucial for the health of our planet. Many of these species play a vital role in maintaining the structure of ecological communities, and their loss can have far-reaching impacts. Through rewilding, we can help to recover these species and ensure their survival.
The reintroduction of native species can also contribute to the fight against climate change. Many of these species, such as trees and seagrasses, can sequester carbon and help to reduce the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Rewilding plays a crucial role in shaping the future of our environment. By allowing nature to take its course, we can restore degraded ecosystems, recover biodiversity, and create more resilient landscapes. Whether it's through ecosystem restoration, environmental rehabilitation, or the reintroduction of native species, rewilding offers a powerful solution to many of the environmental challenges we face today.



.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)