Point of Use Agriculture and Off-Grid Gardening
Point of Use Agriculture is a sustainable approach to growing food that reduces transportation costs, lowers carbon emissions, and ensures that you have fresh and nutritious produce right at your backdoor. Learning how to build a wind garden, solar garden or a raised keystone garden will set you on a path towards a self-sufficient, sustainable lifestyle.
What is Point of Use Agriculture?
Point of Use Agriculture refers to the practice of growing food directly at the place where it is grown picked, prepared, preserved and consumed. One advantage of this stand-alone food production system is that it is saleable; that is to say it can be adopted for container gardens that occupy little space to lager backyard or homestead gardens of an acre of more in size.
Why You Should Build an Off-Grid Garden
Building an off-grid garden is not only a rewarding experience but also a practical solution in world where broken supply chains and the rising cost of food have not only resulted in a lowering of the quality of produce on store shelves but a shortage in some pretty basic items, we eat every day. Here are more reasons why you should consider creating your own off-grid garden:
Self-Sufficiency: By growing your own food, you become less dependent on food shipped in from wherever. This can be particularly beneficial during times of crisis or emergencies when food supply chains may be disrupted.
Health Benefits: Homegrown produce is fresher and more nutritious than store-bought vegetables. You have complete control over the types of fertilizer you use, ensuring that your fruits and vegetables are free from harmful chemicals.
Cost Savings: Growing your own food can help you save money. Once you have set up your point of use off-grid garden, the ongoing costs are minimal compared to a constant run to the market to buy food.
Environmental Impact: By eliminating the need for long-distance transportation and the use of synthetic fertilizers, off-grid gardening helps to lower carbon emissions and minimize the negative impact on the environment.
Homestead Gardens: A Sustainable Approach to Point of Use Agriculture
Homestead gardens are a sustainable approach to point of use agriculture that allows individuals to grow a wide variety of crops and raise livestock on their own property. These gardens typically utilize permaculture principles, such as crop circle farms and gardens, which focus on creating self-sustaining, earth and plant friendly ecosystems. Homestead gardens typically include fruit trees, vegetable beds, herb gardens, and even small-scale animal husbandry, such as goats and chickens.
One of the advantages of homestead gardens is the ability to grow a diverse range of crops. By incorporating companion planting techniques, where different plants are grown together to benefit each other, gardeners can maximize the use of space and create a more resilient and productive ecosystem. Additionally, homestead gardens can be designed to conserve water and promote biodiversity, further enhancing their sustainability.
Another advantage is the elimination of long-distance transportation and reduced dependence on commercial farming practices, dependent on synthetic fertilizers. By growing food locally, individuals can have a direct connection to their food source and have greater control over the quality and freshness of their produce.
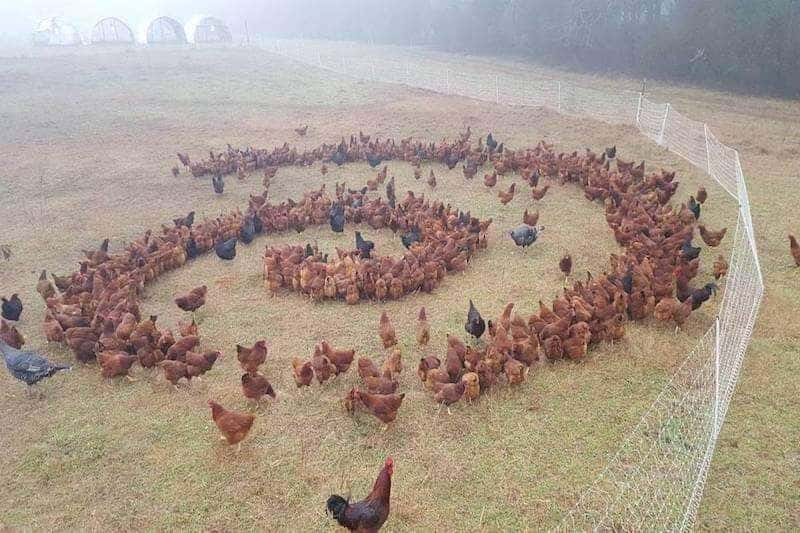
A key aspect of homestead gardens is the integration of livestock. Chickens, for example, can provide fresh eggs and help control pests in the garden by eating insects. In some instances, you can grow chickens and vegetables together using a double spiral pen. Goats or sheep can be used for milk, meat, or fiber production. By including animals in the garden, a holistic and self-sufficient ecosystem can be created, reducing the need for expensive, time-consuming external inputs.
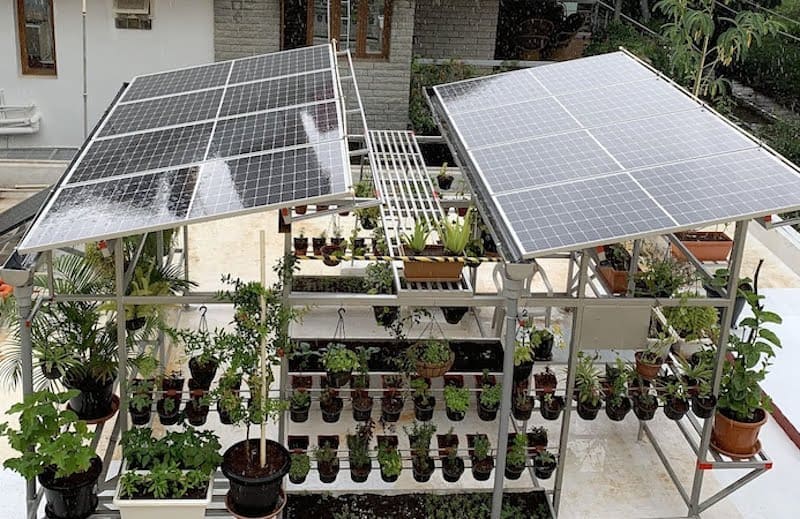
Solar Gardens: Harnessing Solar Energy for Off-Grid Gardening
Solar gardens are an innovative way to harness solar energy for off-grid gardening. By using solar panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, gardeners can power various tools and equipment needed for their garden. Solar energy can be used to run irrigation systems, lighting, and even electric fences for protecting crops from wildlife.
One of the advantages of solar gardens is their sustainability. Solar energy is renewable and abundant, making it an eco-friendly choice for off-grid gardening. Additionally, solar panels have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, making them a cost-effective investment in the long run.
Another advantage is the opportunity to grow shade loving plants like lettuce or spinach, under the panel to create an agrovoltaic system.
To set up a solar garden, gardeners need to determine their energy requirements and design a solar panel system accordingly. It is important to consider factors such as the location of the garden, the amount of sunlight available, how the sun tracks across the sky, he size of the panels needed and whether or not you want to grow plants under the panels. By carefully planning and implementing a solar garden, gardeners can enjoy the benefits of renewable energy, grow shade plants through the heat of the summer, while reducing their carbon footprint.
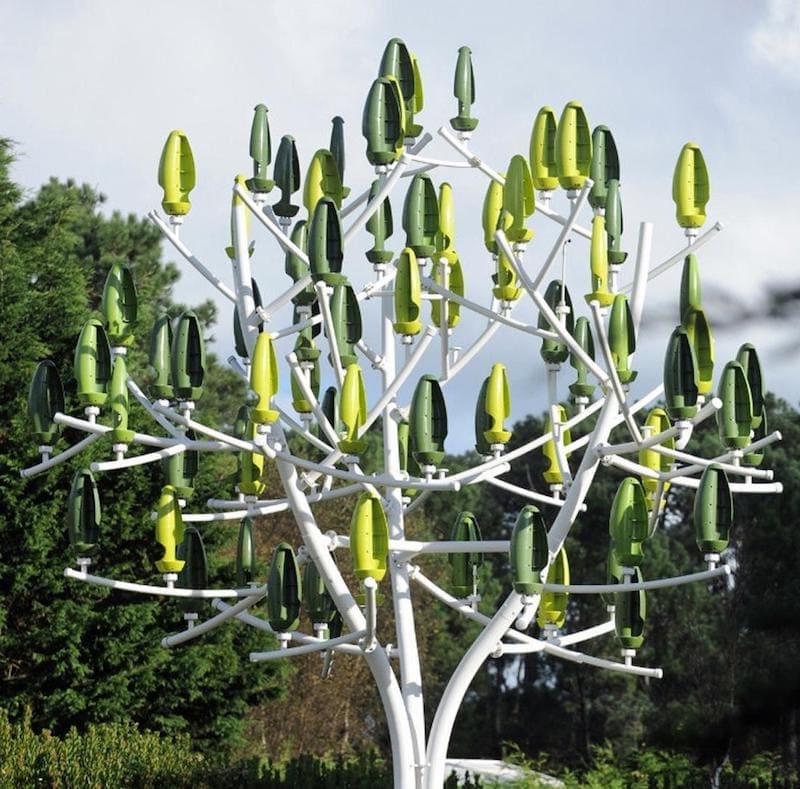
Wind Gardens: Using Wind Power for an Off-Grid Garden
Wind gardens are another alternative for off-grid gardening, harnessing the power of wind to generate electricity. Wind turbines can be used to capture the energy from the wind and convert it into electrical power. This energy can then be used to run various garden equipment, such as water pumps, tools, and electric vehicles.
One of the advantages of wind gardens is that wind energy is abundant and free. Unlike fossil fuels, wind is a renewable resource that does not produce harmful emissions or contribute to climate change. By utilizing wind power, gardeners can reduce their reliance on traditional energy sources and create a more sustainable garden.
Another advantage is to basket the pole that supports the wind turbine. Baskets can be filled with growth medium to grow vegetables (tomatoes), fruits (strawberries), herbs (basil) and flowers (nasturtium).
To set up a wind garden, it is essential to assess the wind potential of the location. Factors such as wind speed, direction, and consistency need to be considered. Additionally, the size and type of wind turbine should be chosen based on the energy requirements of the garden. By investing in a wind garden, gardeners can take advantage of nature's power, trailing and hanging plants, and reduce their environmental impact.
No-Till Agriculture: Minimizing Soil Disruption and Maximizing Plant Production
No-till agriculture is an off-grid farming method that minimizes soil disruption and maximizes plant production. Instead of plowing or tilling the soil, gardeners leave it virtually undisturbed, preserving its structure and nutrients. This method offers several benefits for point of use off-grid gardening:
Water Retention: By leaving the soil undisturbed, no-till agriculture helps to improve water retention. The soil acts as a sponge, absorbing and holding moisture, which is crucial for plant growth, especially in dry climates.
Weed Suppression: Tilling the soil can bring dormant weed seeds to the surface, leading to an increase in weed growth. No-till agriculture helps to suppress weed growth by leaving the soil surface undisturbed, preventing weed seeds from germinating. The addition of a permeable ground cover aids in this effort as well.
Implementing no-till agriculture in an off-grid garden requires careful planning and management. Cover crops or an agricultural grade ground cover can be used to protect the soil and add organic matter. Mulching with organic materials such as straw or wood chips can further enhance soil health and reduce weed growth. By adopting no-till agriculture, gardeners can create a more sustainable and productive garden.
Biodynamics: A Holistic Approach to Off-Grid Gardening
Biodynamics is a holistic approach to off-grid gardening that emphasizes the interconnectedness of all living things. It combines organic farming practices with a spiritual understanding of the natural world. Biodynamic gardening aims to create a self-sustaining ecosystem that respects the rhythms and cycles of nature.
One of the key principles of biodynamics is the use of biodynamic preparations. These preparations are made from natural materials such as herbs, minerals, and animal manure. They are used to enhance soil fertility, stimulate plant growth, and promote overall plant health. Biodynamic practitioners also follow a calendar based on lunar and planetary cycles to determine the optimal times for sowing, planting, and harvesting.
In addition to the use of preparations and lunar cycles, biodynamic gardens often incorporate diverse planting schemes and crop rotations. This helps to promote biodiversity, reduce pest and disease pressure, and maintain soil fertility. Biodynamic gardeners also aim to create a harmonious relationship between plants, animals, and humans, fostering a sense of interconnectedness and balance.
Implementing biodynamics in a point of use off-grid garden requires a deep understanding of natural systems and a commitment to sustainable practices. By embracing this holistic approach, gardeners can cultivate a garden that is not only productive but also in harmony with the natural world.
Implementing Point of Use Agriculture and Off-Grid Gardening Systems
Implementing point of use agriculture and off-grid gardening systems requires careful planning and consideration. Here are a few steps to get started:
Assess Your Space: Determine the available space for your off-grid garden. Consider factors such as sunlight exposure, soil quality, and access to water sources. This will help you decide on the type and size of the garden you can create.
Choose Your Method: Select the off-grid gardening method that suits your needs and resources. Whether it is a homestead garden, a solar garden, a wind garden, or a combination of these, make sure to research and understand the requirements of each system.
Plan Your Garden: Create a detailed garden plan that includes the layout, crop selection, and any additional features such as composting areas or rainwater harvesting systems. Consider companion planting and crop rotation techniques to maximize productivity and reduce pest and disease pressure.
Gather the Necessary Resources: Depending on the chosen method, gather the necessary resources such as seeds, tools, solar panels, or wind turbines. Research and invest in high-quality equipment to ensure the longevity and efficiency of your off-grid gardening system.
Start Small and Expand: It is advisable to start small and gradually expand your off-grid garden as you gain experience and confidence. Growing with garden containers is a great place to start. This will allow you to learn from your successes and challenges and adjust your approach accordingly.
Maintain and Monitor: Regularly maintain and monitor your off-grid garden to ensure its success. This includes watering, weeding, pest control, and soil management. Pay attention to any signs of nutrient deficiencies or plant diseases and take appropriate actions.
Point of Use Agriculture and Off-Grid Gardening offer you the opportunity to take control of your food supply, reduce your environmental impact, and create a more sustainable lifestyle. Whether through homestead gardens, solar gardens, wind gardens, or by implementing practices such as no-till agriculture and biodynamics, you can enjoy the benefits of fresh and nutritious produce while minimizing your reliance on store bought produce trucked in from wherever.




.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)