Innovative Approaches to Sustainable Architecture: The Rise of Biodegradable Shelters
Sustainable architecture is an innovative approach that seeks to minimize the environmental impact of buildings through efficiency and moderation in the use of materials, energy, and development space. It incorporates a variety of strategies during the design, construction, and operation phases to achieve this goal. These strategies include energy efficiency, building material efficiency, and water conservation, among others including using small-foot print, low-impact structures fabricated with bio-degradable materials such as bamboo.
However, sustainable architecture isn't just about conserving resources. It also embraces the concept of creating healthier environments for people to live and work in. By improving air quality, enhancing natural light, and using materials that do not off-gas harmful chemicals, sustainable architecture is likely to improve human health and well-being.
In recent years, the concept of sustainable architecture has evolved beyond the construction of individual green buildings to encompass entire communities and cities, focusing not just on how buildings are designed and constructed, but also on how they interact with each other and the environment.
The Need for Innovative Approaches in Sustainable Architecture
In order to meet the growing demand for sustainable buildings and communities, architects and designers are constantly seeking innovative approaches. These approaches push the boundaries of what is possible in sustainable architecture, from using new materials and technologies, to rethinking the way buildings are designed, constructed and disposed of.
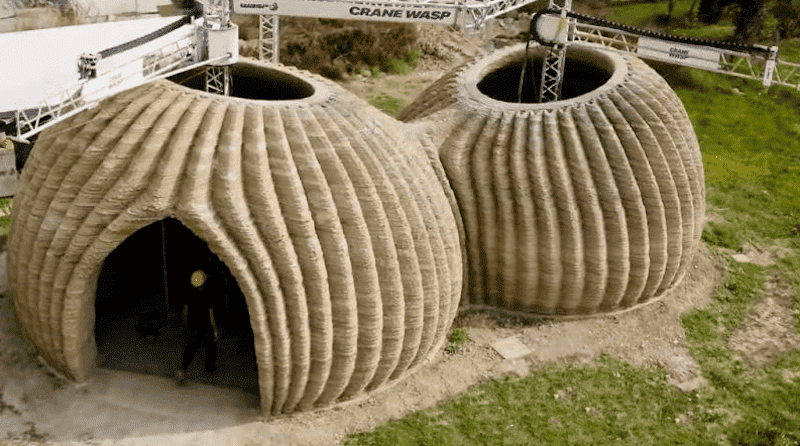
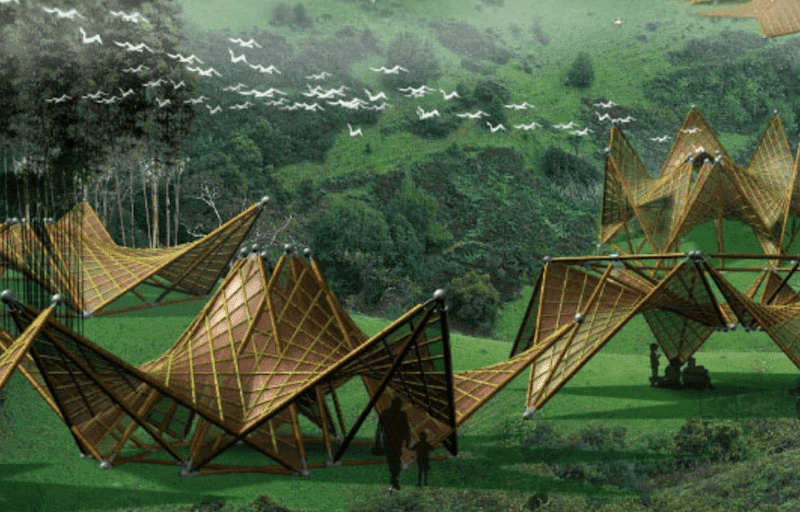
One of the most promising of these innovative approaches is the use of biodegradable shelters. Biodegradable shelters represent an innovative approach to sustainable architecture and emergency housing solutions. These shelters are designed to have a minimal environmental impact, both in terms of the materials used for construction and their lifecycle.
The concept of biodegradable shelters is not entirely new. For centuries, people have constructed temporary shelters from natural materials that eventually decompose and return to the earth.
However, the modern twist on this ancient practice involves using innovative materials and design strategies to create shelters that are not only biodegradable, but also comfortable, durable, and suitable for a variety of uses particularly in emergency situations.
What are Biodegradable Shelters?
Biodegradable shelters are temporary or semi-permanent structures that are designed to decompose naturally over time. They are often used in emergency situations, such as natural disasters or refugee crises, as a quick and environmentally friendly housing solution. However, they can also be used for a variety of other purposes, such as temporary housing for outdoor events or as an innovative approach to sustainable architecture in general.
These shelters are typically constructed from materials that are either naturally biodegradable, such as bamboo, straw, or certain bioplastics, or materials that can be easily recycled or composted. The idea is that once the shelter is no longer needed, it can be disassembled and the materials can be returned to the earth, rather than ending up in a landfill.
In addition to being environmentally friendly, biodegradable shelters are also designed to be affordable and easy to assemble. This makes them an ideal solution for situations where quick, cost-effective housing is needed especially in relief situations.
Materials Used in the Construction of Biodegradable Shelters
The choice of materials is a key aspect of the design and construction of biodegradable shelters. These materials must be durable enough to withstand the elements, yet biodegradable or recyclable in order to minimize the environmental impact.
Natural materials like bamboo, straw, and certain types of wood are commonly used due to their strength, durability, and biodegradability. Bamboo, for example, is a rapidly renewable resource that is strong and flexible, making it an ideal material for shelter construction.
Recycled materials are another important component of biodegradable shelters. These can include recycled plastic, metal, or other materials that can be repurposed into durable, reusable building materials.
The Environmental Impact of Biodegradable Shelters
The environmental impact of biodegradable shelters is significantly lower than that of traditional shelters. This is due to several factors, including the materials used, the design and construction techniques, and the lifecycle of the shelter.
The use of biodegradable or recyclable materials helps to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. Furthermore, because these shelters are designed to be disassembled and returned to the earth, they do not contribute to the problem of abandoned buildings and urban decay.
In terms of design and construction, biodegradable shelters often employ efficient techniques that minimize waste and energy use. This can include modular designs, which allow for components to be pre-fabricated and assembled on-site, reducing the amount of waste produced during construction.
Finally, the lifecycle of a biodegradable shelter is much shorter than that of a traditional shelter. This means that the resources used in its construction are returned to the environment more quickly, reducing impact on the environment.
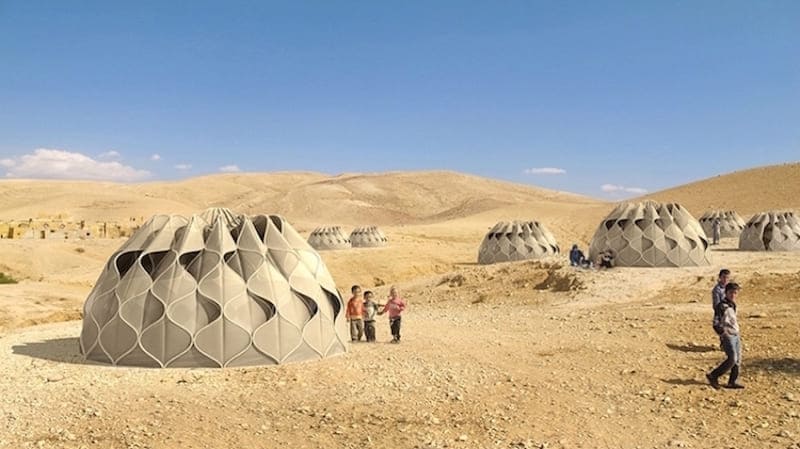
Biodegradable Shelters as an Emergency Housing Solution
In emergency situations, such as natural disasters or refugee crises, the need for quick, affordable housing is essential. Biodegradable shelters offer an innovative solution to this problem by providing a safe, comfortable place to live while minimizing environmental impact. Because these shelters are designed to easily assemble, they can be quickly deployed in the aftermath of a disaster. This can be critical in situations where people have been displaced from their homes and need immediate shelter.
In addition to providing a temporary housing solution, biodegradable shelters can also be used as a longer-term solution in situations where people are unable to return to their home such as in the case of a refugee camp. Because these shelters are designed to be durable and comfortable, they can provide a viable housing option for months or even years.
In addition to natural materials, certain types of bioplastics are also used in the construction of biodegradable shelters. These bioplastics are typically derived from plant material plastics that are designed to break down in the environment over time.
Recycled materials are another important component of biodegradable shelters. These can include recycled plastic, metal, or other materials that can be repurposed into durable, reusable building materials.
The Environmental Impact of Biodegradable Shelters
The environmental impact of biodegradable shelters is significantly lower than that of traditional shelters. This is due to several factors, including the materials used, the design and construction techniques, and the lifecycle of the shelter.
The use of biodegradable or recyclable materials helps to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. Furthermore, because these shelters are designed to be disassembled and returned to the earth, they do not contribute to the problem of abandoned buildings and urban decay.
In terms of design and construction, biodegradable shelters often employ efficient techniques that minimize waste and energy use. This can include modular designs, which allow for components to be pre-fabricated and assembled on-site, reducing the amount of waste produced during construction.
Finally, the lifecycle of a biodegradable shelter is much shorter than that of a traditional shelter. This means that the resources used in its construction are returned to the environment more quickly, reducing impact on the environment.
Biodegradable Shelters as an Emergency Housing Solution
In emergency situations, such as natural disasters or refugee crises, the need for quick, affordable housing is essential. Biodegradable shelters offer an innovative solution to this problem by providing a safe, comfortable place to live while minimizing environmental impact. Because these shelters are designed to easily assemble, they can be quickly deployed in the aftermath of a disaster. This can be critical in situations where people have been displaced from their homes and need immediate shelter.
In addition to providing a temporary housing solution, biodegradable shelters can also be used as a longer-term solution in situations where people are unable to return to their home such as in the case of a refugee camp. Because these shelters are designed to be durable and comfortable, they can provide a viable housing option for months or even years.
The Lifecycle of a Biodegradable Shelter
The lifecycle of a biodegradable shelter begins with the design and construction phase, where materials are selected and the shelter is designed to be easy to assemble and disassemble. Once the shelter is assembled, it can be used for as long as it is needed, whether that is a few days, a few months, or even a few years.
When the shelter is no longer needed, it can be disassembled and the materials can be returned to the earth. This can be done by composting the materials, if they are biodegradable, or by recycling them, if they are recyclable.
The entire lifecycle of a biodegradable shelter is designed to have a minimal environmental impact. From the selection of materials, to the design and construction techniques, to the end of the shelter's life, every aspect is designed with sustainability in mind.
The Rise and Future of Biodegradable Shelters in Sustainable Architecture
Biodegradable shelters represent a new and exciting direction in sustainable architecture. As the need for sustainable housing solutions continues to grow, it is likely that the use of biodegradable shelters will continue to rise.
Looking to the future, there are many exciting possibilities for biodegradable shelters. Advances in materials science could lead to the development of new, more durable and biodegradable materials. Improvements in design and construction techniques could make these shelters even more efficient and affordable.
The Potential of Biodegradable Shelters for Sustainable Architecture
There have been several successful biodegradable shelter projects around the world. For example, in the aftermath of the 2010 earthquake in Haiti, a team of architects and designers created a series of biodegradable shelters using bamboo and other natural materials. These shelters provided a quick, affordable, and environmentally friendly housing solution for those displaced by the disaster.
Another example is the "B Home" project in India, which provides temporary shelters for homeless individuals. These shelters are constructed from recycled materials and are designed to be easy to assemble and disassemble.
Biodegradable shelters represent an innovative and promising approach to sustainable architecture. They offer a viable solution to the pressing need for affordable, sustainable housing, especially in emergency situations. With their minimal environmental impact and potential for future development, biodegradable shelters hold great potential for the future of sustainable architecture and temporary housing.




.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)