The Growing Crisis in Asia: China Running Out of Food and Water?
China, the world's most populous country, is currently facing a pressing crisis - a shortage of food and water. This crisis has far-reaching implications not only for the Chinese people but also for the global economy. In this blog, we will explore the factors contributing to this crisis, the consequences it is already having, and the urgent need for sustainable agricultural technologies to address the situation.
Factors Contributing to the Crisis, Resource Exploitation, Dams Flooding Farmland, Environmental Degradation and Pollution
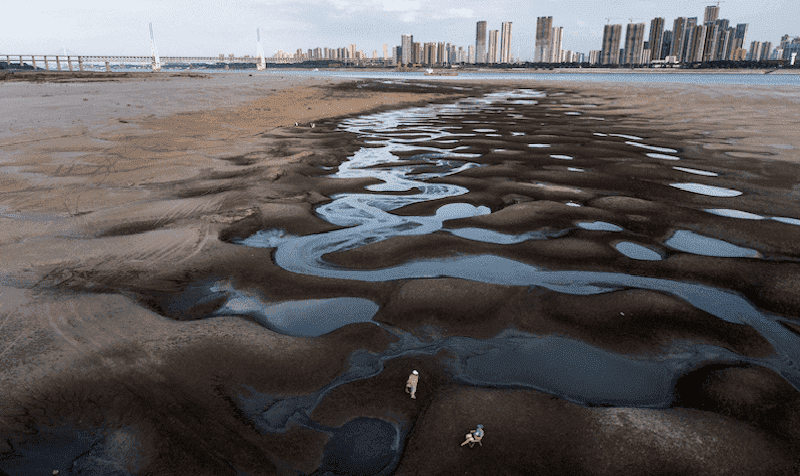
One of the primary factors contributing to China's food and water crisis is the rampant exploitation of its natural resources. Rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to increased demand for resources, resulting in the overuse and depletion of water sources and arable land. The excessive extraction of groundwater for agricultural and industrial purposes has caused water tables to plummet, making it increasingly difficult for farmers to irrigate their crops adequately.
Another significant factor exacerbating the crisis is the construction of large dams across the country, such as The Three Gorges across the Yangtze River. While dams provide hydroelectric power and help control flooding, they also flood vast areas of farmland. The displacement of farmers and the loss of fertile land have had detrimental effects on China's ability to grow food for its own people. The construction of these dams has disrupted traditional farming practices and forced many farmers to abandon generational livelihoods.
China's rapid economic growth has come at a steep environmental cost. Pollution from industrial activities, including factory emissions and untreated wastewater, has contaminated water sources, making them unsafe for consumption and agricultural use. In addition deforestation, and soil erosion have further degraded the quality of arable land. These environmental issues have significantly hindered China's agricultural productivity and contributed to the current crisis.
A Growing Number of Chinese are Suffering
The food and water crisis in China is not an abstract issue; it is affecting the lives of millions of Chinese citizens. As food prices continue to rise, many families find it increasingly difficult to afford nutritious meals. This situation disproportionately impacts low-income households, who may be forced to compromise on the quality and quantity of food they consume. Moreover, water scarcity has become a daily reality for many communities, leading to hygiene and sanitation problems. The lack of access to clean water poses severe health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly.
Consequences of the Crisis, Rising Food Prices, Water Scarcity, Social Unrest
The shortage of food in China has resulted in a significant increase in food prices. As supply struggles to meet demand, the cost of basic food items, including grains, vegetables, and meat, has soared. This rise in prices puts a strain on household budgets and exacerbates existing inequalities, as those with limited financial resources find it increasingly difficult to afford an adequate diet. The inflationary pressures caused by rising food prices also have broader economic implications, as they can lead to higher overall inflation rates and reduced consumer spending power.
China's water crisis is characterized by severe scarcity in many regions. This scarcity not only affects individuals and households but also has a detrimental impact on agriculture, industry, and energy production. Water-intensive sectors such as industrialized agriculture and manufacturing face significant challenges in securing sufficient water supplies to sustain their operations. Additionally, the lack of water for energy generation poses a threat to China's power supply, potentially leading to disruptions in electricity distribution. The water scarcity issue in China is a multi-faceted problem that requires immediate attention and sustainable solutions.
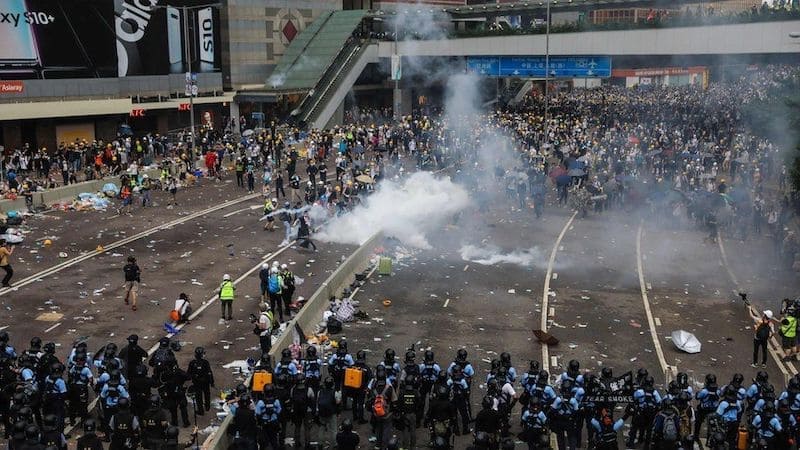
The food and water crisis in China has the potential to fuel social unrest. As citizens face rising food prices, water scarcity, and reduced access to basic necessities, frustration and discontent can grow. In the past, food shortages and price spikes have led to protests and social unrest in various parts of the country. The Chinese government recognizes the risks associated with social instability and is keen to address the crisis before it escalates into a larger problem.
The Urgent Need to Adopt Sustainable Agricultural Technologies
To address the growing crisis of food and water scarcity in China, it is crucial to adopt sustainable agricultural technologies. These technologies can help increase agricultural productivity while minimizing the negative environmental impact. Practices such as precision agriculture like Crop Circle Farms, drip irrigation, and organic farming can help conserve water resources, protect soil fertility, and reduce the use of harmful agrochemicals. Investing in research and development of these technologies, as well as promoting their widespread adoption, will be essential to ensure long-term food and water security in China.
If immediate and effective action is not taken, China is on a path to run out of food and water. Factors such as resource exploitation, dam construction, industrialized agriculture, environmental degradation, and pollution have contributed to this crisis. Rising food prices, water scarcity, and the potential for social unrest are among the immediate consequences. To mitigate these challenges, urgent action is needed to adopt water-smart agricultural technologies that can enhance productivity while preserving the environment.



.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)