Growing Plants with Ingeniously Designed Water Storage Depressions
Water is a precious resource, and ensuring its availability for plants is crucial for sustainable agriculture. One innovative solution to this challenge is the use of artificially created water storage depressions. These depressions collect and store water, providing plants with a reliable source of hydration even during dry periods. In this article, we will explore the benefits of using water storage depressions for plant growth, the techniques involved in creating them, and their role in re-building subterranean ecosystems.
The benefits of using water storage depressions for plant growth
Water storage depressions, crafted to gather and conserve water for vegetation, bring a host of benefits. Their foremost advantage lies in providing a reliable water source, diminishing dependence on erratic rainfall and manual irrigation. This is particularly valuable in dry areas where water is scarce, as it ensures plants have access to necessary hydration even during periods of drought, fostering their growth and resilience.
Additionally, these depressions are instrumental in promoting water conservation. They capture rainwater runoff, reducing wastage and facilitating more efficient water use. This approach not only aids in plant sustenance but also plays a critical role in preserving water resources. In a world increasingly concerned with water scarcity, the adoption of such innovative methods is crucial for the sustainable development of agriculture.
Cavitated plant cultivation and its impact on water conservation
Cavitated plant cultivation, a method incorporating water storage depressions, is a notable advancement in sustainable agriculture. This technique involves the creation of soil cavities around plant roots, functioning as mini reservoirs. Utilizing specific tools, these cavities are carefully positioned around the root zone. They gather and retain water, gradually releasing it into the surrounding earth, thereby maintaining consistent moisture levels for the plants.
The impact of cavitated plant cultivation on water conservation is significant. By concentrating water storage at the roots, it significantly cuts down on evaporation and unnecessary water loss. This precision in watering not only leads to considerable water savings but also ensures efficient use of water resources. Furthermore, the conserved water acts as a safeguard during periods of drought, supporting plant growth and reducing the risk of water scarcity for the plants.
Innovative techniques for creating water storage soil cavities
Innovative methods for crafting water storage soil cavities have recently been developed. Root Tubes represent one such approach. By inserting these tubes into the ground, vertical pathways are formed, channeling water straight to a plant's roots. These tubes are adept at evenly spreading water, ensuring consistent moisture while averting the risk of waterlogging.
Crop Circle Irrigators are another emerging technique. These involve crafting circular basins around plants to gather and retain water. The round design promotes effective water dispersal, guaranteeing thorough hydration for the entire plant. What makes crop circle irrigators particularly appealing is their adaptability, as they can be tailored to various plant types and watering needs, offering a flexible approach to water storage.
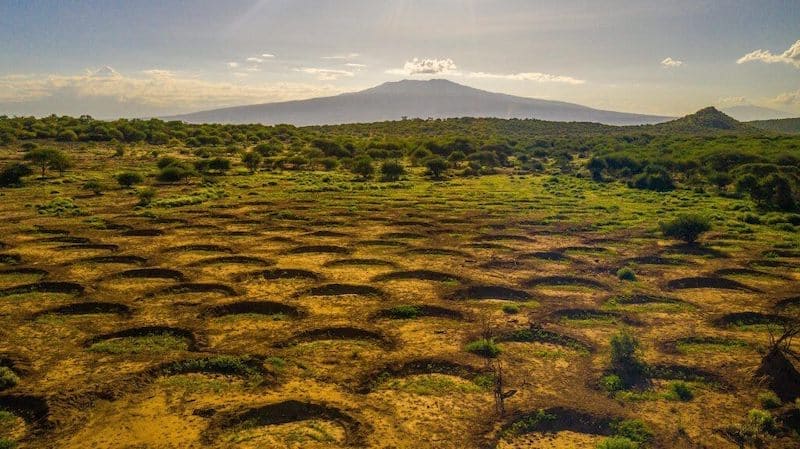
Another strategy involves the creation of semi-circular indentations in the soil. These half-moon shaped depressions are especially useful in drought-prone regions, as they collect and hold rainwater during the wet season.
The role of water storage depressions in re-building subterranean ecosystems
Water storage depressions not only benefit plant growth but also play a vital role in re-building subterranean ecosystems. These depressions create microhabitats that support diverse underground organisms, such as earthworms and beneficial microbes. These organisms contribute to soil health and fertility, enhancing overall ecosystem resilience.
By promoting the growth of subterranean organisms, water storage depressions improve soil structure and nutrient cycling. They facilitate the movement of water and nutrients through the soil profile, ensuring their availability to plants. This symbiotic relationship between plants and subterranean organisms creates a thriving ecosystem that is essential for sustainable agriculture.
Implementing water storage depressions in to collect and store water for higher yield
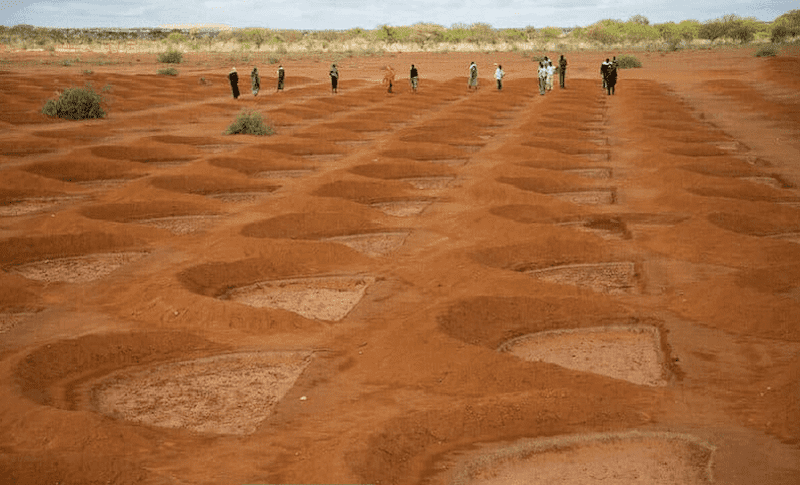
The term "half-moon rainwater depressions" refers to a specific type of water conservation technique commonly used in arid and semi-arid regions. These depressions are crescent-shaped pits dug into the earth, designed to capture and store rainwater. The unique shape and strategic placement of these depressions help in maximizing water collection, especially during scarce rainfall periods. They are often aligned on the contours of sloping land, which allows them to intercept runoff water efficiently. This technique not only aids in water conservation but also helps in soil moisture retention, crucial for plant growth in dry areas.
For instance, in the Sahel region of Africa, where water scarcity is prevalent, half-moon rainwater depressions have been effectively used to combat desertification and improve agricultural productivity. Farmers dig these depressions in their fields before the rainy season. When the rains come, the depressions fill with water, which slowly percolates into the soil, providing moisture for crops long after the rains have stopped. In Burkina Faso, this technique has transformed barren lands into productive fields, enabling communities to grow crops such as millet and sorghum, which are staples in their diet. Similarly, in parts of India, half-moon rainwater depressions have been used to revitalize parched lands, allowing for the cultivation of vegetables and other crops, thus improving food security and livelihoods in rural areas.
Resources and tools for designing and building water storage depressions
Various resources and tools are accessible for farmers and gardeners interested in creating water storage depressions in agricultural settings. Online resources, such as agricultural forums and platforms, offer insights into new techniques and established best practices. For practical implementation, there are specialized suppliers that farmers and gardeners can access that provide an array of equipment, including both mechanical and manual diggers, as well as root tubes and crop circle irrigators.
Staying updated with the latest developments in water storage technology is crucial. This can be achieved through participation in workshops, webinars, and conferences focused on sustainable agriculture and water conservation. For instance, Crop Circle Farms provides video tutorials demonstrating the installation of their irrigators and root tubes. Continually enhancing their knowledge helps farmers and gardeners make well-informed decisions, ensuring the effective establishment of water storage depressions in gardens and farms.
Harnessing the power of water storage depressions for sustainable plant growth
Artificially created depressions that collect and store water for plants offer a promising solution for sustainable agriculture. They provide a consistent water supply, reduce reliance on rainfall and irrigation, and promote water conservation. Techniques like cavitated plant cultivation, root tubes, and crop circle irrigators enable efficient water usage and contribute to increased crop yield.
Water storage depressions also play a crucial role in re-building subterranean ecosystems, enhancing soil health, and supporting diverse underground organisms. By implementing these innovative techniques farmers and gardeners can contribute to the sustainable growth of plants and ensure a more resilient agricultural system even in the driest of climates.



.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)