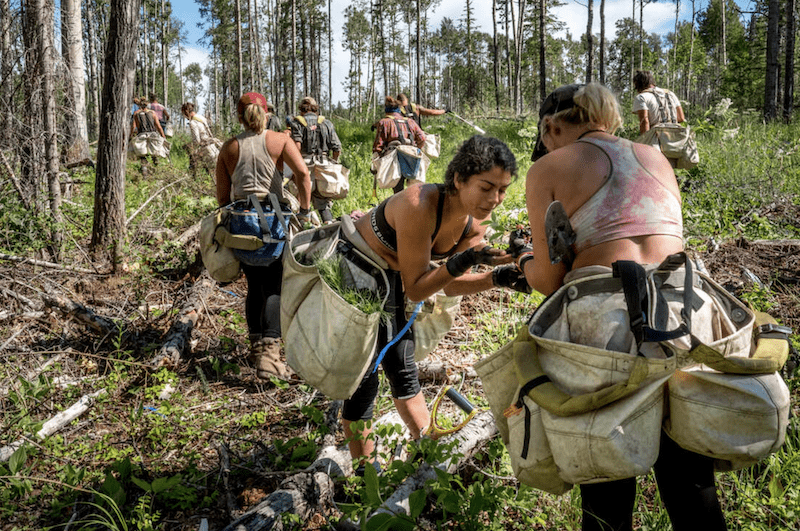
A Donation for Climate Change: How planting tall tree seedlings quickly reduce the effects of climate change
Planting tall tree seedlings to create instant forests where there where none before can help reduce the effects of global warming and combat climate change in several ways:
CARBON SEQUESTRATION: Carbon sequestration is a process where trees soak up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and contain it within their branch and trunk structure, contributing to a decrease in the volume of greenhouse gases in the air. This process aids in alleviating global warming effects by minimizing the presence of gases that trap heat in the atmosphere.
COOLING EFFECT: Tall tree seedlings that create instant forests can also help to reduce the effects of global warming by providing shade and cooling. Instant forest leaf canopies soak up sunlight and cast shade, a feature that can decrease temperatures in city environments and lessen the impact of the urban heat island phenomenon.
WATER CONSERVATION: The planting of tall tree seedlings to create an instant forest plays a critical role in regulating the water cycle by intercepting rainfall, reducing runoff, and recharging groundwater. This can assist in lessening the effects of droughts and diminishing the likelihood of flood events.
BIODIVERSITY CONSERVATION: Tall tree seedlings provide habitat for a wide range of plant and animal species. By creating an instant forest, we can help to protect biodiversity and promote ecosystem resilience, which is important for adapting to the impacts of climate change inclusing changing rainfall patterns.
The creation of an instant forest is a crucial environmental assets that aid in diminishing the consequences of global warming and confronting climate change. Through the transplanting of 10-foot-tall tree seedlings, we can soften the blows of climate change, fostering a more sustainable future for us and generations to come.
Beyond Softwoods: The Critical Role of Hardwoods in Climate Mitigation
The predominant tree planted to mitigate the effects of climate change are softwoods, but we need to plant more hardwoods. Reforestation and afforestation efforts aimed at lessening the impact of climate change frequently utilize softwood trees like pine and spruce. Softwoods are generally fast-growing and can sequester large amounts of carbon quickly.
It's equally important to note that hardwood trees hold significance in reforestation and afforestation initiatives intended to counteract climate change. Hardwood species like oak, maple, and beech not only have longer lifespans than softwoods, but they also have the capacity to sequester carbon for many decades, and in some cases, centuries. Hardwoods are also typically more diverse in their benefits to wildlife and the environment.
While softwoods may be more common for afforestation and reforestation projects, it is important to consider planting hardwood species as well to ensure the ecological diversity of forest ecosystems. For fostering long-term carbon sequestration and biodiversity, it's advised to employ a diverse array of species, incorporating both softwoods and hardwoods.
Benefits of Diversified Tree Planting: The Dual Role of White Pine and Yellow Birch
A great way to promote biodiversity and enhance the ecological benefits of forest ecosystems is to grow white pine and yellow birch and yellow birch together in a forest reclamation project. White pine is a fast-growing softwood tree that can sequester carbon quickly and is often used for reforestation projects. It provides valuable timber and is also an important habitat for wildlife. Contrastingly, yellow birch, a type of hardwood tree, grows at a slower pace and has the capacity to live for many decades, possibly even centuries. It is also valuable for timber and provides important habitat for a range of wildlife species. These two trees are habitually found growing together in their natural habitat around the Great Lakes of North America.
Growing red oak, red pine, and sugar maple together in a tree plantation provides a wide range of benefits. Red oak, a significant hardwood species, serves as an essential living space for numerous wildlife species. It is also a popular timber species and is known for its strength and durability. On the other hand, red pine, a rapidly growing softwood species, is frequently employed in reforestation endeavors. It can sequester carbon quickly and is also valuable for timber. Sugar maple is another hardwood species that provides important habitat for wildlife and is also known for its beautiful fall foliage. By growing red oak, red pine, and sugar maple together in a plantation, we can create a more diverse and resilient forest ecosystem.. The different tree species can help to support a wider range of wildlife and promote a healthier and more sustainable forest environment. Moreover, instant forests with a variety of species typically exhibit greater resistance to pests and diseases, compared to monoculture plantations which tend to be more vulnerable to such outbreaks.
How Growing To Give Reclaims Swamps and Wetlands Planting Tall Black Cherry and Cedar Trees
Reclaiming swamps and wetlands by planting black cherry and cedar trees would help fight climate change, restore, and protect aquatic ecosystems and provide nesting areas for birds like the red-winged blackbird, the common tern, herons, dusks, and geese. A host of creatures live in swamps and wetlands, and all are vitally important to a diversified ecosystem and surprisingly have a role to play in combating climate change.
A multitude of fish species depend on wetlands for reproduction, sustenance, and refuge. Not only are wetlands essential reproductive environments for numerous amphibian species, like frogs, toads, and salamanders, but they also offer habitats for various species of reptiles, including turtles and snakes like the Painted Turtle, Snapping Turtle, and Eastern Garter Snake. Furthermore, wetlands accommodate a broad array of invertebrates, spanning insects, snails, and worms. These organisms play important roles in nutrient cycling and food webs within the wetland ecosystem.
Black cherry, a type of hardwood tree, exhibits adaptability to various soil conditions, encompassing those found in wetlands and swamps. It provides important habitat for wildlife and is also valuable for timber. Cedar trees are also suitably adapted to marshy environments and can aid in fortifying the soil while inhibiting erosion. By planting tall black cherry and cedar tree seedlings in wetlands and swamps, we could help to restore these areas and provide important habitat for wildlife. In wetlands, trees also possess the ability to cleanse and refine water, potentially enhancing the quality of water in neighboring rivers and streams.


.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)